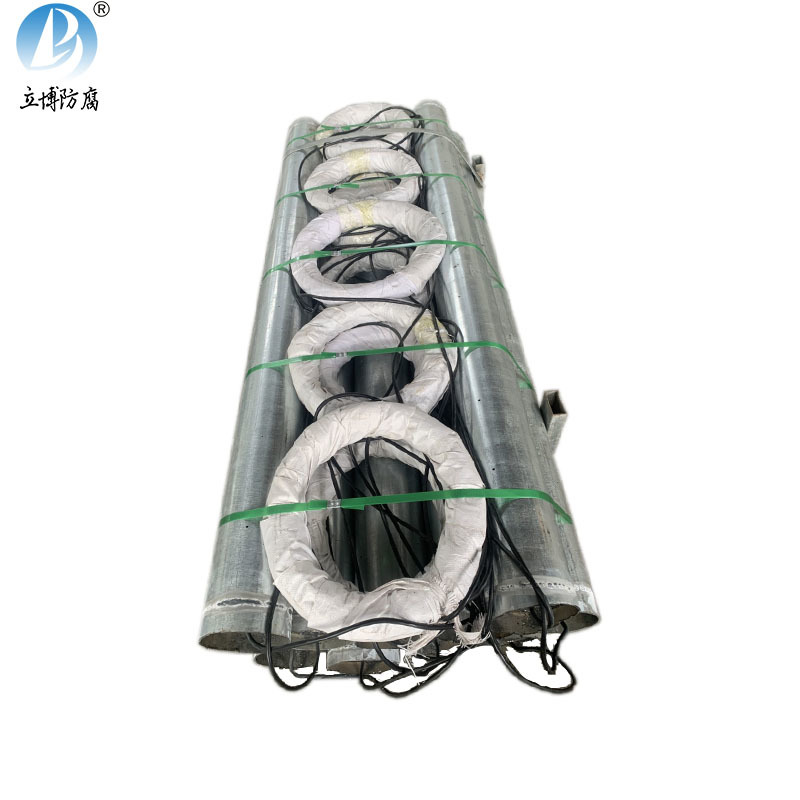
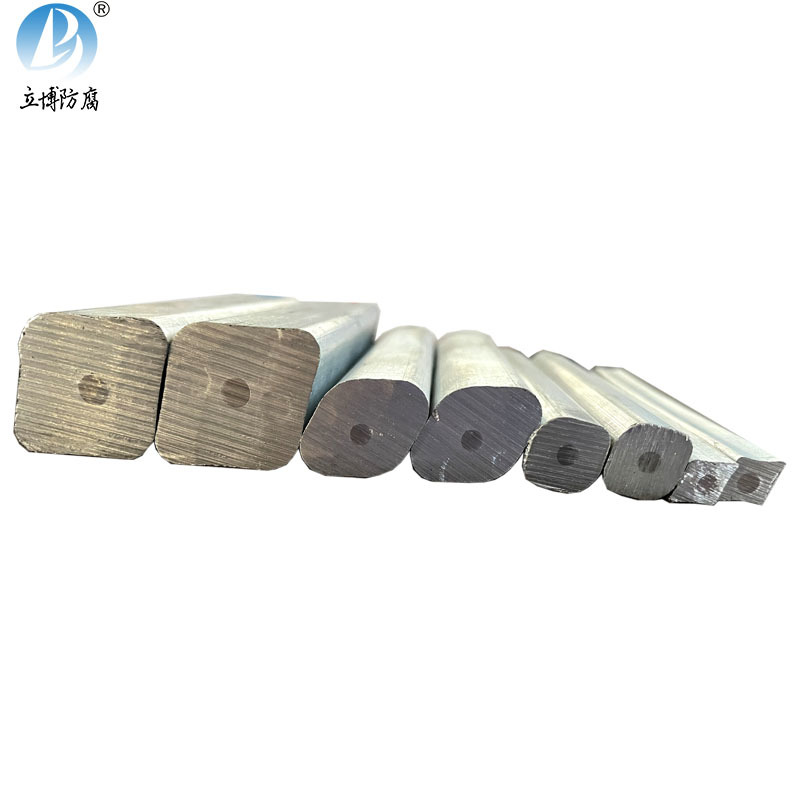
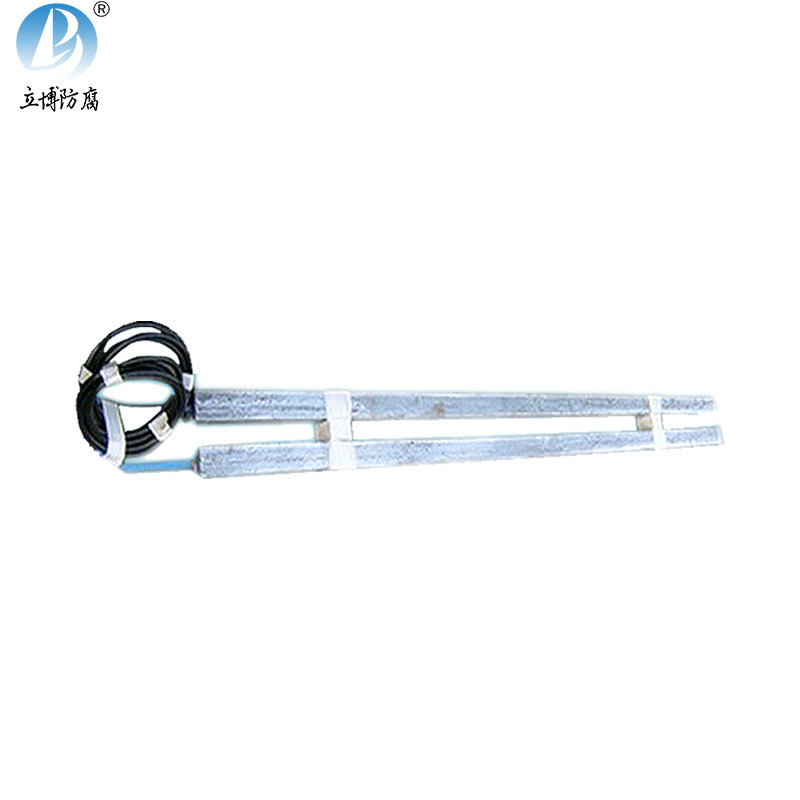
Quality Assurance
Supports multiple specifications customization

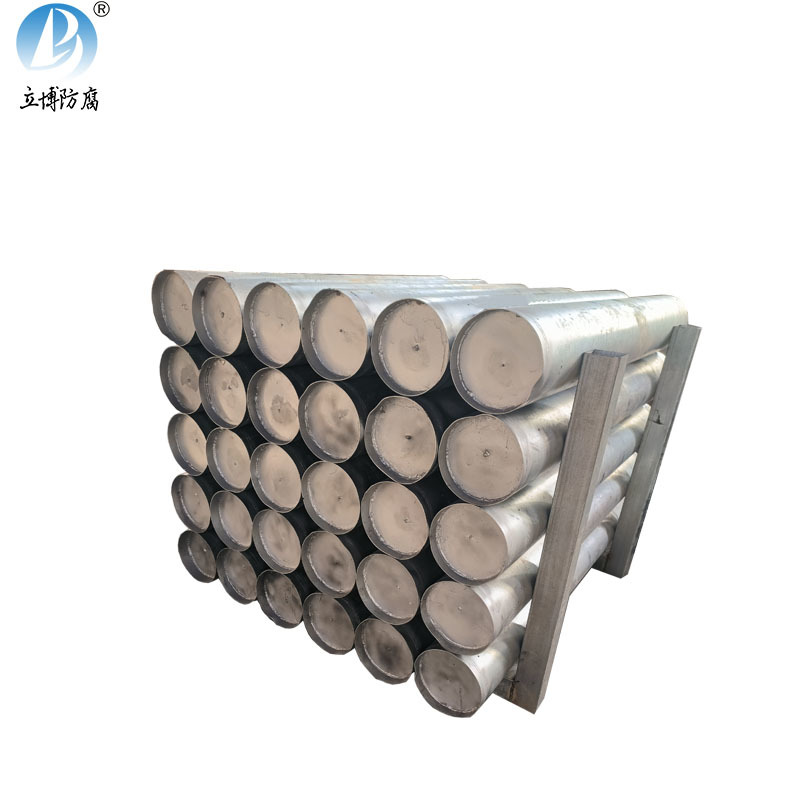
Product Details
Product Parameters
Execution Standards:GB/T4950-2021 GB/T21448-2017
Main Performance: Low anode self-dissolution, high current efficiency, good self-regulation performance of anode current; long protection lifespan, up to 20-30 years, generally no 'over-protection' phenomenon occurs.
Applicable Scope:Zinc alloy sacrificial anodes are suitable for cathodic protection of metal corrosion in ships, ballast water tanks, mechanical equipment, marine engineering and port facilities, drilling platforms, port docks, condensers, water pumps in seawater media, and pipelines, cables, etc. in low resistivity soil.
Product Features:Zinc-aluminum-cadmium (ZAC) sacrificial anodes are cast from high-purity zinc and aluminum, cadmium alloy. This product is recognized by China Classification Society (CCS), and the quality standards meet GB/T4950-2021 standards. The chemical composition of zinc anodes complies with USMIL-A-18001H and ASTM+B418 (Type 1) standards. The anodes for pipelines also comply with GB/T21448-2017 'Design Specification for Cathodic Protection of Buried Steel Pipelines'. Different specifications and sizes can be customized according to customer requirements!
Zinc-aluminum-chromium alloy sacrificial anode
Chemical Composition
Chemical Elements | AI | Cd | Impurities not greater than | Zn | |||
Fe | Cu | Pb | Si | ||||
Content % | 0.3-0.6 | 0.05-0.12 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.125 | Remainder |
Electrochemical Performance
| Open Circuit Potential | Working Potential | Actual Electric Capacity | Current Efficiency | Dissolution Status |
In Seawater | -1.09~-1.05 | -1.05~-1.00 | ≥780 | ≥95 | Corrosion products are easy to detach |
In Soil | ≤-1.05 | ≤-1.03 | ≥530 | ≥65 |
Common Sacrificial Anode Models and Specifications for Hulls
Model | Specification | Weight (kg) |
Length*Width*Height (mm) | ||
ZH-1 | 800*140*60 | 47.0 |
ZH-2 | 800*140*50 | 39.0 |
ZH-3 | 800*140*40 | 31.0 |
ZH-4 | 600*120*50 | 25.0 |
ZH-5 | 400*120*50 R | 16.0 |
ZH-6 | 500*100*40 | 13.6 |
ZH-7 | 400*100*40 | 11.0 |
ZH-8 | 300*100*40 | 7.5 |
ZH-9 | 250*100*40 | 6.5 |
ZH-10 | 180*70*40 | 3.5 |
ZH-11 | 300*150*50 Double Iron Legs | 14.5 |
ZH-12 | 300*150*40 Double Iron Legs | 11.5 |
ZH-13 | 300*150*50 Bolt Type | 12.0 |
ZH-14 | 300*150*40 Bolt Type | 9.0 |
Common Sacrificial Anode Models and Specifications for Port Facilities and Marine Engineering
Model |
| Weight (kg) |
Length*(Upper Base + Lower Base)*Height (mm) | ||
ZI-1 | 1000*(115*135)*130 | 115.0 |
ZI-1 | 750*(115+135)*130 | 85.0 |
ZI-1 | 500*(115+135)*130 | 56.0 |
ZI-1 | 500*(105+135)*100 | 40.0 |
Common Sacrificial Anode Models and Specifications for Ballast Water Tanks
Model | Specification | Weight (kg) |
Length*(Upper Base + Lower Base)*Height (mm) | ||
ZT-1 | 500*(115+135)*130 | 56.0 |
ZT-2 | 1500*(65+75)*70 | 50.0 |
ZT-3 | 500*(110+130)*120 | 50.0 |
ZT-4 | 1000*(58.5+78.5)*68 | 33.0 |
ZT-5 | 800*(56+74)*65 | 25.0 |
ZT-6 | 1150*(48+54)*51 | 20.0 |
ZT-7 | 250*(80+100)*85 | 13.0 |
ZT-8 | 200*(70+90)*70 | 7.5 |
Bracelet Type Zinc Alloy Anode Models and Specifications
Model | Specification | Weight (kg) |
Inner diameter * Width * Thickness * Gap mm | ||
ZZ-1 | 1020*200*35*51 | 179.5 |
ZZ-2 | 819*60*30*51 | 34.5 |
ZZ-3 | 624*80*30*51 | 45.0 |
ZZ-4 | 513*100*30*51 | 45.0 |
ZZ-5 | 280*250*45*51 | 76.5 |
ZZ-6 | 252*250*45*51 | 68.5 |
Common sacrificial anode model specifications for storage tanks
Model | Specification R | Weight (kg) |
Length*(Upper Base + Lower Base)*Height (mm) | ||
ZC-1 | 750*(115+135)*130 | 85.0 |
ZC-2 | 500*(115+135)*130 | 56.0 |
ZC-3 | 500*(105+135)*100 | 40.0 |
ZC-4 | 300*(105+135)*100 | 25.0 |
Common long strip sacrificial anode model specifications and common disc-shaped sacrificial anode model specifications for seawater cooling water systems
Model | Specification | Weight (kg) |
Length*(Upper Base + Lower Base)*Height (mm) | ||
ZE-1 | 500*(115+135)*130 | 56.0 |
ZE-2 | 1000*(80+100)*80 | 50.0 |
ZE-3 | 500*(105+135)*100 | 40.0 |
ZE-4 | 500*(80+100)*80 | 25.0 |
ZE-5 | 400*(110+120)*50 | 16.0 |
ZE-6 | 300*(140+160)*40 | 12.5 |
ZE-7 | 200*(90+110)*40 | 5.5 |
Model | Diameter * Height (mm) | Weight (kg) |
ZE-8 | 300*60 disc-shaped | 30.0 |
ZE-9 | 360*40 disc-shaped | 28.5 |
ZE-10 | 300*40 disc-shaped | 20.0 |
ZE-11 | 200*50 disc-shaped | 10.5 |
ZE-12 | 180*50 disc-shaped | 8.5 |
ZE-13 | 120*100 disc-shaped | 7.5 |
Common sacrificial anode model specifications for buried pipelines, storage tank outer walls, and other underground metal structures
Model | Specification | Weight (kg) |
Length*(Upper Base + Lower Base)*Height (mm) | ||
ZP-1 | 1000*(78+88)*85 | 50.0 |
ZP-2 | 1000*(65+75)*65R | 33.0 |
ZP-3 | 800*(60+80)*65 | 25.0 |
ZP-4 | 800*(55+64)*60 | 22.0 |
ZP-5 | 650*(58+64)*60 | 18.0 |
ZP-6 | 550*(58+64)*60 | 15.0 |
ZP-7 | 600*(52+56)*54 | 12.5 |
ZP-8 | 600*(40+48)*45 | 9.0 |
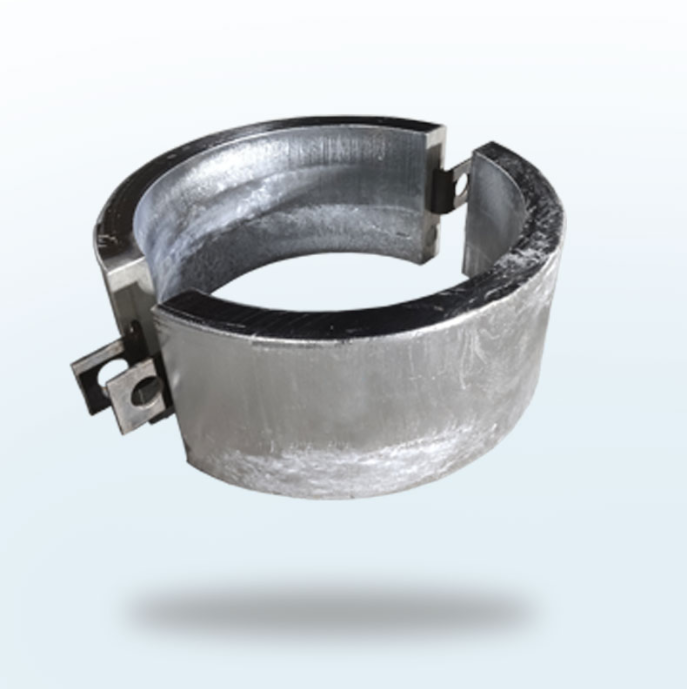
As global offshore energy, subsea infrastructure, and marine transportation industries continue expanding into deeper waters and harsher environmental conditions, the demand for high-performance cathodic protection systems has increased significantly. Among the various solutions available today, the bracelet-type zinc anode has become one of the most widely adopted and technically reliable forms of sacrificial anodes for pipelines, risers, and underwater steel structures.
Bracelet-type zinc anodes—often manufactured in semi-cylindrical pairs and mechanically fastened around pipelines—are specifically engineered to deliver long-lasting galvanic protection. These anodes are commonly installed on subsea pipelines, offshore platforms, jackets, manifolds, and marine risers, where continuous exposure to seawater would otherwise lead to severe corrosion, structural deterioration, and costly maintenance shutdowns.
One of the primary reasons for the growing popularity of bracelet-type zinc anodes is their excellent performance in saltwater environments. Zinc’s natural electrochemical properties make it highly effective as a sacrificial material, providing predictable dissolution and stable potential output over extended periods. Compared with aluminum or magnesium anodes, zinc performs reliably in colder waters and low-oxygen conditions, making it an ideal choice for subsea applications in regions such as the North Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and West Africa.
In engineering design, bracelet-type zinc anodes stand out due to their robust mechanical strength and precise dimensional tolerances. Modern manufacturing processes include advanced alloy formulation, heat treatment, computer-assisted casting, and ultrasonic quality inspection. These technologies ensure that each anode delivers consistent electrochemical performance and withstands the physical stresses associated with deepwater installation and pipeline operation. Many manufacturers now offer custom-engineered anode designs to match specific pipe diameters, coating systems, design life requirements, and offshore project standards.
Beyond corrosion protection, bracelet-type zinc anodes also contribute to improved operational safety and reduced lifecycle costs. By minimizing corrosion-related failures, they help prevent pipeline leaks, environmental pollution, and unplanned equipment downtime. A properly engineered zinc anode system can extend the operational lifespan of subsea pipelines by decades, offering a significant financial advantage to energy companies, offshore operators, and government infrastructure projects. As global energy transitions accelerate, the role of durable corrosion protection materials becomes even more essential.
The market for bracelet-type zinc anodes has grown significantly from 2023 to 2025, driven by large-scale offshore oil and gas development and the rapid expansion of offshore wind energy. Undersea power cables and support structures in offshore wind farms require effective galvanic protection to maintain long-term reliability. Zinc anodes have become a standard component in these installations due to their predictability, compliance with industry standards, and proven corrosion resistance.
In addition, developing regions across Asia, Africa, and Latin America are investing heavily in subsea pipeline networks for natural gas, potable water, and industrial transport. This infrastructure boom has further accelerated the global demand for high-quality bracelet-type zinc anodes. As environmental regulations become stricter, industries are increasingly required to implement protective systems that prevent corrosion-induced leaks and structural degradation, reinforcing the importance of sacrificial anode technologies.
Looking ahead, advancements in material science and manufacturing automation are expected to further enhance the performance of bracelet-type zinc anodes. New alloy formulations promise greater efficiency and slower consumption rates, while digital monitoring systems may allow for real-time evaluation of anode performance. These innovations will strengthen the long-term reliability of subsea assets and help industries operate sustainably in challenging marine environments.
In summary, the bracelet-type zinc anode has established itself as a foundational element in modern corrosion protection engineering. Its durability, stability, and adaptability make it indispensable for offshore pipelines, marine infrastructure, and large-scale subsea projects. As global industries continue moving toward deeper waters and more complex installations, the demand for high-performance zinc anode systems will remain strong, ensuring safe and efficient operation for decades to come.
Bracelet-type zinc anode

Key words:
Bracelet-type zinc anode
Classification:
Recommend products
The company's main products: magnesium alloy sacrificial anode series, aluminum alloy sacrificial anode series, zinc alloy sacrificial anode series, and cathodic protection supporting products, such as more than a dozen varieties and hundreds of specifications.
Focus on the development and production of cathodic protection materials
online message
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your phone or email.







 Performance/Type/Index
Performance/Type/Index